

If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to comment below.The scope of this tutorial is to explain how we can edit and make changes to Network Configurations on RHEL/CentOS 8/7 from the command line only, and, more specifically how we can set up a Static IP address on network interfaces using system network-scripts, which is a must be configured to serve Internet-facing network services, and how to configure or change RHEL/CentOS system hostname.

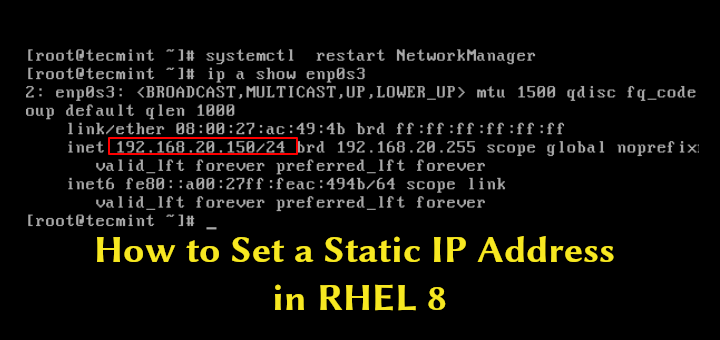
In this guide, we’ve shown you how to configure a static IP in RHEL 7/8 and CentOS 7/8 using two different methods. Valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever Closing Notes Once you modified, run the below command to shut down the interface and bring it back: # ifdown enp0s3 & ifup enp0s3Ĭheck if the new configurations are populated by using ip command: # ip a show enp0s3
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
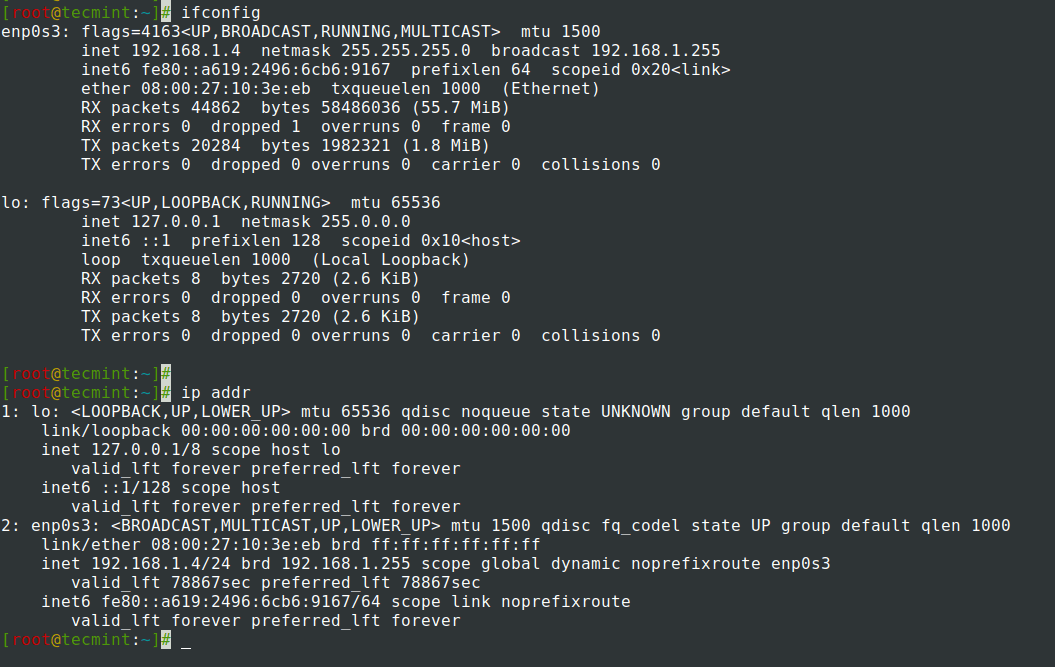
To do so, add or modify the above lines in the following configuration file. These files are named with the "ifcfg-" prefix and the name of the interface.įor instance, to configure a static IP address for “enp0s3” with the following details, see the below steps: IP address = 192.168.1.70 When the system boots, it uses these files to determine what interfaces to bring up and how to configure them. Valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever Method-2: Assign a static IP address by editing network scripts files on CentOS 7/8 and RHEL 7/8įor each network interface, a configuration file is created under the ‘/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts’ directory, which controls the interfaces for individual network devices. You can double confirm, if the new IP address is banded with the interface “enp0s3” by using ip command. To view the details, run: # cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3 All the new configuration has been saved permanently to the file “etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3”. You have successfully configured the interface “enp0s3” with static IP. To save these changes and to reload the interface, run: # nmcli con up enp0s3 To view detailed DHCP configuration of enp0s3, run: Inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe97:132e/64 scope linkĪs we can see from the above output, We have an interface named "enp0s3", which has a dynamic IP. # ip aġ: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 Identifying interfacesīefore proceeding to configure a static IP address, use the ip command to identify all the available Ethernet interfaces on your system. It is used to create, display, edit, delete, activate, and deactivate network connections. The nmcli is a command line tool, which is used for controlling NetworkManager and reporting network status. Method-1: Configure a static IP address using nmcli command on CentOS 7/8 and RHEL 7/8 Static IP address can be configured on Red Hat system using below two methods: In this article, we’ll demonstrate how to assign or configure Static IP address on RHEL 7/8 and CentOS 7/8 Server’s. Suggested Read: How to add secondary IP address on RHEL/CentOS 8.It can be assigned through DHCP (Dynamic Network Configuration Protocol) by either your ISP or your router.īut, you should assign a static IP address to the Linux servers that are accessible through internet.Īlso, large organizations use static IP to avoid network issues due to the unavailability of DHCP servers. Dynamic IP can be used in home system or Local Area Network (LAN) because they are only used internally.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
